The diverse and vast field of metalwork owes a significant amount of its progress to one element in particular: Aluminum. This remarkable metal has firmly established itself as a material of choice in various industries due to its unique and exceptional set of properties. Aluminum exhibits a remarkable combination of lightweight, high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and superb thermal conductivity, making it highly versatile and widely used across a wide range of applications.
What sets Aluminum apart is its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, allowing it to be used in applications where strength is essential but weight is a concern. Furthermore, Aluminum can be easily formed, machined, and welded, making it highly adaptable to different manufacturing processes. Its excellent corrosion resistance ensures durability even in harsh environments, while its exceptional thermal conductivity makes it an ideal material for heat exchange applications.
In the realm of metal bending, Aluminum’s malleability and ductility make it an ideal choice. It can be easily bent, shaped, and formed into intricate designs, allowing for the creation of complex and aesthetically pleasing metalwork. This versatility, combined with its wide availability and cost-effectiveness, has made Aluminum the most usable metal in the industry.
As we delve deeper into the factors that contribute to Aluminum’s prominence in the realm of metalwork, we uncover a fascinating world of innovation, engineering excellence, and limitless possibilities. Join us on this exploration into the captivating realm of aluminum and discover why it continues to be a driving force in the evolution of metalwork.
Why Is Aluminum The Most Usable Metal?
Aluminum stands out as the most usable metal for several compelling reasons. First and foremost, its outstanding malleability makes it an ideal material for metal bending processes. It can be fashioned into a wide variety of shapes without cracking or breaking, making it an extremely versatile choice for numerous applications. Second, Aluminum is noted for its exceptional lightness in comparison to many other metals, which can be a crucial factor in industries where weight matters, such as aerospace or automotive.
A third advantage is its natural resistance to corrosion.
Aluminum forms an oxide layer when exposed to air, which protects it from rust and degradation. This characteristic makes it a preferred choice for outdoor installations and other applications exposed to weather or moisture. Lastly, Aluminum is an excellent conductor of both heat and electricity, making it invaluable in industries like electronics and power distribution. In summary, aluminum’s unique combination of malleability, lightness, durability, corrosion resistance, and conductivity make it an incredibly adaptable and usable metal in a multitude of industries.[1]
Properties and advantages of aluminum
Reflectivity
Aluminum’s reflectivity is a remarkable trait that greatly contributes to its widespread usage. Not only does this property enhance the aesthetic appeal of products made from the metal, but it also holds numerous practical applications across various industries.
For instance, in the lighting industry, Aluminum is highly sought after for its ability to effectively reflect light, making it a popular choice for light fixtures and reflectors. By maximizing the efficiency of the lighting solution, Aluminum not only enhances the overall performance but also reduces energy consumption, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Moreover, the remarkable reflectivity of aluminum extends its utility to the realm of solar technology. In solar panels, Aluminum is utilized to optimize the capture of solar energy, making it an essential component in the production of efficient and sustainable solar power systems.
Non toxic features
Another prominent feature of aluminum that bolsters its usability is its non-toxic nature. Aluminum is not only safe and non-hazardous, but it is also free from any toxic substances that could pose a threat to human health. This means that it doesn’t produce any harmful gases or emit any toxic elements, ensuring utmost safety in its usage. As a result, Aluminum is an excellent choice for applications that involve direct contact with food or beverages, making it highly suitable for use in the food packaging and culinary industries. Examples of Aluminum’s safe use can be seen in everyday items such as Aluminum cans, foil, and kitchen utensils. Furthermore, due to its exceptional non-toxic qualities, Aluminum is extensively utilized in the manufacturing of medical devices and equipment, proving its worth and reliability in healthcare settings. Therefore, the non-toxic characteristics of Aluminum not only enhance its versatility but also make it highly applicable across a wide range of industries, ensuring the well-being and safety of both consumers and healthcare professionals alike.
Recyclability
The recyclability of Aluminum is not only integral to its broad use and sustainability but also a key factor in reducing environmental impact. Unlike many other materials, Aluminum can be recycled indefinitely without any loss in quality or integrity. This means that once Aluminum is extracted from the earth, it can be reused continuously, reducing the need for new mining and further preserving natural resources. Additionally, the process of recycling Aluminum requires only 5% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum, making it a highly energy-efficient choice. From beverage cans to automotive parts, the use of recycled aluminum not only offers the same performance as new Aluminum but also significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with its production.
As industries increasingly recognize the importance of sustainable practices, the use of recyclable materials like Aluminum underscores their commitment to environmental stewardship and a greener future.
Strength
The strength of Aluminum is not only a key factor but also one that greatly contributes to its widespread use. Despite its lightweight nature, Aluminum possesses remarkable strength and durability, making it highly suitable for a wide range of high-stress applications. Whether it’s the construction of towering buildings and expansive bridges or the manufacturing of reliable automobiles and advanced aircraft, Aluminum proves to be an exceptional choice due to its ability to withstand substantial forces and pressures. This is attributed to the specific alloy and processing techniques employed, which further enhance its strength. The high strength-to-weight ratio of Aluminum sets it apart from many other materials, solidifying its position as a versatile and invaluable resource in numerous industries. It is this exceptional combination of strength, durability, and lightweight design that truly distinguishes Aluminum as a premium choice for various applications.
High strength-to-weight ratio
The high strength-to-weight ratio of Aluminum is a crucial attribute that truly separates it from other materials. While it is considerably lighter than many other metals, it doesn’t compromise on strength. The excellent strength-to-weight ratio makes it a preferred choice in industries like automotive and aerospace where weight is a concern. Lighter vehicles and aircraft equate to greater fuel efficiency, which not only reduces costs but also lessens environmental impact. In construction, the strength-to-weight ratio allows for the building of sturdy yet lightweight structures, resulting in increased safety, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. Therefore, this high strength-to-weight ratio of Aluminum significantly broadens its applications, making it a go-to material for industries aiming for efficiency and sustainability.
Ease of fabrication
The ease with which Aluminum can be fabricated is yet another reason why it is widely favored across industries. Aluminum is a remarkably malleable metal, meaning it can be easily formed, shaped, and manipulated into a variety of forms and designs. Its ductility allows it to be drawn into thin wires or extruded into complicated cross-sectional profiles – a property hugely beneficial in industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and construction. Furthermore, Aluminum’s machinability is superior to many other metals, which means it can be effectively cut, drilled, and milled using simple tools. This ease of fabrication not only makes Aluminum a cost-effective option but also provides designers and manufacturers the freedom to innovate and create complex, high-performance products.
Ductility
Aluminum’s exceptional ductility is yet another remarkable characteristic that greatly accentuates its usability. Ductility, in the context of materials, refers to the ability to undergo deformation under tensile stress. In simpler terms, it means that Aluminum can be effortlessly stretched into a thin wire without the fear of it breaking. This remarkable property of Aluminum not only sets it apart but also enables its seamless transformation into a diverse range of shapes and sizes, without compromising its inherent properties or performance.

This outstanding feature finds practical applications in various sectors, with electronics being a prime example. Aluminum wires, thanks to their remarkable ductility, are extensively utilized in electronics, facilitating the efficient flow of electric current. In addition, in the realm of construction, Aluminum’s ductility plays a pivotal role in enhancing the resilience of infrastructure. When subjected to seismic activities, aluminum’s ability to flex under stress rather than shatter allows structures to withstand and absorb the impact, contributing to the creation of more durable and robust buildings.
Therefore, the remarkable ductility of aluminum not only widens its array of applications but also further solidifies its status as a highly sought-after material, valued for its exceptional properties and versatility.
Strength at low temperatures
Aluminum’s performance at low temperatures is yet another factor that boosts its desirability. Unlike many other materials, Aluminum does not become brittle at low temperatures. Instead, it retains its strength or even becomes stronger, making it a critical material in industries such as aerospace and cryogenics that often deal with extreme cold conditions. This attribute means that structures or components made from aluminum can safely endure the rigors of extremely cold environments without a loss in structural integrity. Hence, the strength of Aluminum at low temperatures further expands its use in a multitude of applications, solidifying its position as one of the most versatile and reliable materials available today.
Impermeable and odorless
A further advantage of Aluminum is its impermeability and odorlessness, which make it an ideal material for food and beverage packaging. Aluminum’s impermeable nature ensures that no light, oxygen, or moisture can reach the product, maintaining its freshness and preserving its flavor over a longer period. Moreover, being odorless, aluminum does not react with the packed foods or beverages, avoiding any foreign taste. This combination of properties is why you often see drinks, dairy, and ready-to-eat meals packed in Aluminum containers. Therefore, the impermeable and odorless characteristics of Aluminum further extend its usability in industries that prioritize hygiene and product preservation.
Non-magnetic
One of the often-overlooked advantages of Aluminum is that it is non-magnetic. This feature makes it the material of choice for many applications where magnetism could interfere with the performance or safety of a product. For instance, in the field of electronics, components made from Aluminum do not interfere with the device’s electromagnetic fields, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Similarly, in medical imaging, Aluminum is used in the construction of devices such as MRI machines because its non-magnetic nature does not distort the magnetic fields required for imaging. Hence, the non-magnetic characteristic of Aluminum adds another layer to its appeal, increasing its suitability for a broader range of industries and applications.[2]
Uses of Aluminum in industry
The applications of Aluminum in various industries are vast and diverse due to its unique properties. Its lightweight nature, excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, and high strength-to-weight ratio make it a highly sought-after material. From aerospace and automotive industries to construction and packaging, aluminum finds its uses in making aircraft, cars, buildings, cans, and many more products. Its versatility and recyclability further contribute to its widespread adoption across different sectors, making it an indispensable material in modern manufacturing processes.[3]
Energy Industry
The industry also capitalizes on the beneficial properties of Aluminum. In renewable energy sectors, particularly solar and wind, aluminum’s durability, light weight, and resistance to corrosion make it an excellent choice for constructing various components. For example, in solar panels, Aluminum frames are commonly used to house the photovoltaic cells. The use of Aluminum ensures that the panels can withstand various weather elements without significant wear, thus enhancing their longevity and performance. Similarly, in wind energy, the lightness of Aluminum contributes to the efficiency of wind turbine blades.
Moreover, the high conductivity of Aluminum makes it a preferred material for power transmission lines. Its exceptional conductivity allows for efficient and reliable power distribution, while its lighter weight and lower cost compared to copper make it a more economical choice. Hence, the unique attributes of Aluminum significantly contribute to its widespread application in the energy industry, reaffirming its essential role as a versatile and valuable metal.Food Industry
In the food industry, Aluminum’s impermeability, odorlessness, and resistance to corrosion make it a highly preferred material for packaging and preserving food products. The impermeable nature of Aluminum ensures an airtight seal, preventing any external elements such as light, oxygen, or moisture from penetrating the packaging. This effectively maintains the freshness, flavor, and nutritional value of the food products, while also extending their shelf life.
Furthermore, the odorless characteristic of Aluminum plays a crucial role in preserving the authentic taste of food items. Unlike other materials, Aluminum does not react with food products or introduce any foreign taste or odor. This ensures that the flavor profile of the food remains unaltered, allowing consumers to enjoy the true essence of the culinary experience.
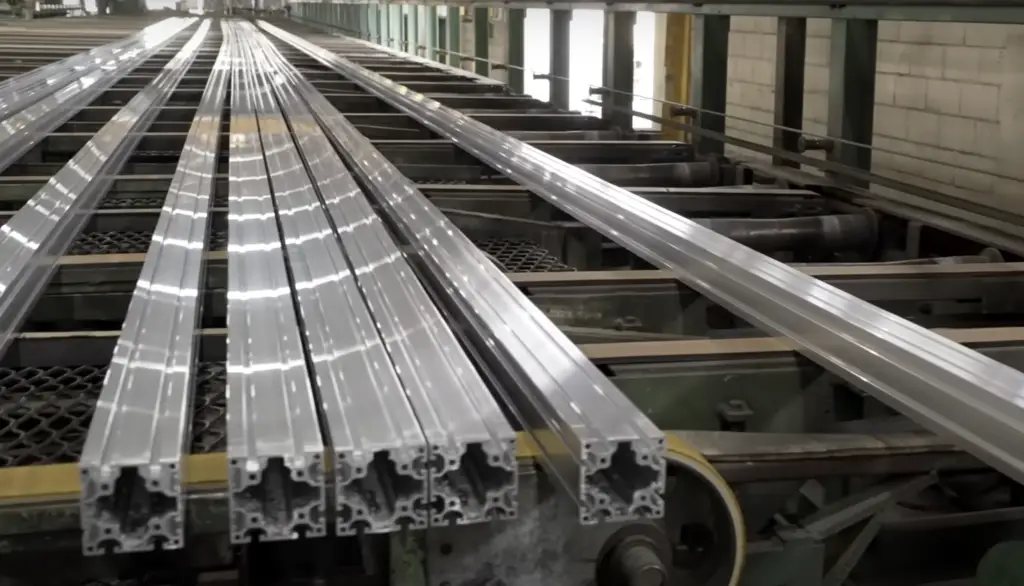

The unique properties of Aluminum, combined with its safety for direct contact with food, have contributed to its widespread use in the food industry. Whether in the form of cans for drinks and ready-to-eat meals, trays for baking, or foil for wrapping, Aluminum serves various purposes in packaging, preserving, and even cooking food. Its versatility and reliability have made it an irreplaceable metal in the industry.
Therefore, it can be concluded that Aluminum’s exceptional properties not only ensure optimal preservation of product quality but also contribute to its status as a highly usable metal in the food industry.
Construction Industry
In the world of construction, Aluminum finds extensive application due to its unique combination of physical properties. Its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it an excellent choice for structures that need to be robust but lightweight. Buildings, bridges, and tunnels often utilize aluminum in their design for this very reason. Furthermore, its resistance to corrosion ensures that structures made with aluminum can withstand the elements without significant wear or degradation, a critical factor in construction projects. This corrosion resistance also allows for less maintenance over the lifespan of the structure, making aluminum a cost-effective material in the long run. Additionally, Aluminum’s malleability and ease of fabrication make it a versatile choice, capable of being shaped into a variety of forms to meet the specific needs of a project. From roofing and window frames to structural elements in skyscrapers, Aluminum’s adaptability is truly unmatched in the construction industry. Therefore, whether it’s for its strength, lightness, corrosion resistance, or versatility, Aluminum’s attributes render it an irreplaceable tool in the toolbox of the construction industry.
Transportation Industry
The transportation industry also finds Aluminum indispensable due to its unique combination of attributes. Aluminum’s lightweight nature paired with its high strength makes it ideal for applications in automobiles, trains, and marine vessels. Its lightweight contributes to fuel efficiency in vehicles, reducing their environmental impact. In railway applications, aluminum is used in overhead lines, providing a cost-effective and durable solution.
By using Aluminum, manufacturers can create lighter, more fuel-efficient, and robust vehicles, contributing to a more sustainable transportation industry. Therefore, Aluminum’s properties not only make it a highly usable material in this sector but also play a huge role in promoting eco-friendly transportation solutions.FAQ
Why is Aluminum used the most?
Aluminum stands out from other metals due to its diverse range of properties that make it applicable in various industries. Its lightweight nature, combined with its impressive strength, presents a unique advantage in sectors such as construction and transportation, where weight and durability are of major concern. Aluminum’s resistance to corrosion extends its lifespan in many applications, reducing the need for frequent replacement and thus proving cost-efficient in the long run. Additionally, its non-magnetic nature is advantageous in the electronics and healthcare industries, as it prevents interference with the functioning of devices. Its high conductivity makes it a key player in the energy sector, while its impermeability and odorlessness are critical for its usage in the food industry. In essence, the wide usage of aluminum can be attributed to its versatility and ability to meet the unique needs of different industries. Its contribution to sustainability initiatives, such as in energy-efficient vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure, also boosts its popularity in our increasingly eco-conscious society.
Why is Aluminum preferred over Steel?
There are several reasons why Aluminum is often preferred over steel. First and foremost, Aluminum is significantly lighter than Steel. This makes it an ideal choice for applications where weight is a crucial factor, such as in transportation and aviation. Lighter vehicles mean better fuel efficiency and lower emissions, contributing to more sustainable transportation solutions. Secondly, Aluminum displays a greater resistance to corrosion.

Unlike Steel, which can rust over time, Aluminum creates its own protective oxide layer, making it far more enduring in corrosive environments. This quality makes it a preferred choice in maritime applications and outdoor constructions. Additionally, the ease of working with Aluminum, its malleability, and the ability to recycle it without any loss of its original properties, further give aluminum an edge over Steel.
Why is Aluminum used more than Copper?
While Copper has its own strengths, such as high electrical conductivity, it falls short when compared to Aluminum in certain aspects. Aluminum is often favored over Copper due to its lighter weight and lower cost. While both metals are good conductors of electricity, Aluminum is significantly lighter, making it a preferred choice for power transmission over long distances. The reduced weight leads to cost savings in support structures, towers, and other infrastructure. Furthermore, Aluminum is cheaper and more abundant than Copper, which makes it a more economical choice for many industries. The malleability and ductility of Aluminum also mean it can be formed into various shapes and sizes, adding to its versatility over copper. Lastly, while Copper tends to corrode by producing a green patina, Aluminum forms an oxide layer that is highly resistant to corrosion. These factors contribute to the preference for aluminum over copper in many applications.
Why is Aluminum strong?
Despite its lightweight nature, Aluminum boats considerable strength, a feature that makes it a popular choice across various industries. This strength can be attributed to its unique crystalline structure, which is tightly packed and allows the molecules to resist external forces. Aluminum’s strength can also be enhanced through different processes. For instance, alloying it with other metals such as copper or manganese can significantly increase its tensile strength. Moreover, heat treatment methods can also be used to alter the metal’s microstructure, resulting in enhanced strength. Thus, the inherent strength of Aluminum, combined with its ability to be easily enhanced through various processes, contributes to its widespread application in industries where both weight and strength are critical factors.
Why is Aluminum better for the environment?
Aluminum’s environmental credentials further enhance its standing as a preferred metal in various industries. Notably, Aluminum is recyclable, maintaining its original properties even after numerous recycling cycles. This characteristic reduces the need for fresh extraction of the metal, thereby saving energy and mitigating negative environmental impact.

The energy required to recycle Aluminum is a mere fraction of that needed for its initial extraction, making the recycling process highly energy-efficient. Moreover, the light weight of Aluminum reduces energy consumption in transportation applications, which in turn decreases Carbon emissions. Aluminum also plays a crucial role in the renewable energy sector, with its high conductivity and corrosion resistance making it ideal for use in solar panels and wind turbines. Therefore, the eco-friendly characteristics of Aluminum, including its recyclability, energy efficiency, and applications in the renewable energy sector, reinforce its status as an environmentally preferable metal.
Useful Video: IMS Comparing Aluminum Alloys
Conclusion
In conclusion, the versatility, durability, and eco-friendly nature of Aluminum have cemented its status as a preferred metal across various industries. Its unique properties, such as its lightweight nature, strength, and resistance to corrosion, not only fulfill the diverse needs of different sectors but also contribute significantly to sustainability initiatives. Whether it’s powering our homes, enabling us to travel, or housing our food and drink, Aluminum’s role is far-reaching. Its ability to be recycled without any loss of its original properties further underscores its importance in a world increasingly conscious of its environmental footprint. Indeed, as we strive towards a more sustainable future, it’s clear that Aluminum will continue to be a key player in our journey.
References:
- https://markhammetals.com/why-is-aluminum-the-most-usable-metal/
- https://www.thyssenkrupp-materials.co.uk/advantages-of-aluminium.html
- https://avionalloys.com/top-3-industrial-uses-aluminum/






