Do you find it difficult to decide between titanium and aluminum? You’re not alone. Both metals possess incredible properties that make them invaluable to a range of industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, medical devices & equipment, jewelry-making and more. In this blog post we’ll look at the unique advantages of both while weighing up their differences in order to determine which metal is truly better for your specific needs — Titanium or Aluminum? So if you’ve been struggling for guidance on which choice to go with then let us explain the benefits and drawbacks each has so that you can make an informed decision about what’s best for your application.
What Is Titanium?
Titanium is a lightweight, silver-gray metal that is strong and corrosion resistant. It has a low density but high strength-to-weight ratio and is often used in the aerospace, automotive, medical device, petrochemical and nuclear industries.
In addition to its superior durability and strength, titanium also offers several advantages over aluminum including lower weight, better corrosion resistance and higher temperature tolerance. Its resilience makes it an ideal material for applications where reliability is of paramount importance.In comparison to aluminum, titanium offers greater strength while maintaining light weight qualities; it is up to 30% stronger than aluminum with only half the weight of steel. Titanium has excellent corrosion resistance and does not corrode in sea water or other harsh environments, making it ideal for use in marine and aerospace applications. Additionally, titanium is biocompatible and non-toxic, which makes it an ideal material for medical implants and prosthetics.

Despite its many advantages, titanium is a relatively expensive metal compared to aluminum due to the difficulty of extraction from ore and processing into usable forms. It also requires specialized welding techniques that can result in extra costs associated with fabrication. [1]
What Is Aluminum?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal with many desirable properties. It is malleable and ductile, making it easy to shape or form into different shapes. Aluminum is suitable for use in electronics and heat transfer due to its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. Finally, aluminum offers excellent corrosion resistance, so it can be used for products that must hold up in harsh environments.
Titanium vs. Aluminum: Which Metal Is Better?
Titanium and aluminum are both popular metals, used in a variety of applications. But which one is better? It really depends on your needs. To help you decide, let’s take a look at the differences between titanium and aluminum:
When it comes to strength, titanium is the clear winner. Titanium is much stronger than aluminum, making it ideal for applications that require a lot of durability or high strength-to-weight ratio. However, this comes with a tradeoff – titanium is also more expensive than aluminum so it may not be suitable if cost is an issue.
Aluminum has its own advantages as well. It’s lightweight and corrosion resistant, which makes it great for construction projects or outdoor applications. Aluminum is also cheaper than titanium, which can be beneficial if you’re on a budget.

When it comes to aesthetics, both metals have their own unique look. Titanium has a darker hue that gives it a modern and sleek appearance while aluminum tends to be more silver in color with a bit of shine.
So which metal is better – titanium or aluminum? Ultimately, the choice depends on your needs and budget. Titanium is stronger and more durable but also more expensive, so if cost isn’t an issue then it may be the better choice. Otherwise, aluminum offers its own advantages at a much lower price point. No matter what metal you choose, make sure to consider all the factors before making your final decision.
Pros and Cons of Titanium
One big advantage of titanium as a metal is that it is incredibly lightweight. It weighs 45% less than steel, but has the same strength. This makes it an extremely desirable metal for companies needing to make products that are light in weight yet strong enough to last. Titanium is also corrosion-resistant, making it the ideal choice for applications where exposure to water and other elements could cause rapid deterioration. Additionally, titanium’s high melting point makes it suitable for use in extreme temperatures.
However, titanium does come with some downsides as well. For one thing, its production costs tend to be much higher than most other metals due to its rarity. Also, when compared to aluminum alloys, titanium alloys can be quite expensive and difficult to fabricate. Additionally, titanium has poor electrical conductivity and is not ideal for applications that require the efficient transfer of electricity. Lastly, titanium’s fatigue strength is lower than aluminum alloys, meaning it can be more prone to fracturing over time under repeated stress.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight metal that is easy to transport and relatively inexpensive. It is widely used in construction, manufacturing, and other industries because of its strength-to-weight ratio, malleability, ductility, resistance to corrosion, electrical conductivity properties, and reflectivity.
These qualities allow for a variety of uses such as structural products for bridges and buildings, cans and packaging materials, components of cars and planes. Aluminum has become the preferred material for many projects due to its durability combined with a lower cost than steel or titanium.[2]
However, aluminum does have some drawbacks when compared to other metals like titanium. For instance, it is not as strong or hard as steel or titanium so it may not be suitable for certain applications where a higher level of strength is required. Additionally, aluminum can be susceptible to fatigue and cracking if not properly treated or cared for. Finally, aluminum does corrode more easily and requires regular maintenance to keep it from rusting and corroding quickly. For these reasons, Aluminum may not be suitable for certain projects which require metal with an increased durability.
In conclusion, while Aluminum offers many advantages over other metals such as lower cost and weight, it has some drawbacks that should be taken into consideration when selecting the appropriate material for a project. Aluminum may not always provide the desired performance when compared to more durable metals like steel or titanium.
Maintenance Tips for Titanium
Titanium is a highly durable metal that is used in a variety of applications due to its strength and resistance to corrosion. Despite its durability, there are some maintenance tips you should consider if you use titanium in any of your products or projects.
- Clean the surface regularly. Titanium can get easily dirtied from dust and other particles that it comes into contact with. It’s always best to keep the surface clean by washing it off with water as often as necessary.
- Use lubrication when needed. If you’re using titanium screws, adding a bit of lubrication can help reduce friction and make sure that the screws don’t become stuck over time. This will also help to increase the product’s overall lifespan.
- Avoid contact with acidic substances or solutions. Titanium is highly resistant to corrosion, but it can still be affected by certain acidic substances and solutions. Make sure that any liquids, cleaning agents, or chemicals you use are pH neutral so as not to damage the titanium surface.
- Regularly inspect for signs of wear and tear. Even though titanium is very durable, it can still suffer from general wear and tear over time if not properly maintained. Inspect your products regularly for signs of damage or deterioration in order to minimize risk and extend their life span as much as possible. [3]
Maintenance Tips for Aluminum
Aluminum is a popular metal for use in construction and consumer goods, due to its strength and lightweight. However, aluminum does require some maintenance in order to maximize its lifespan. Here are some tips to help you keep your aluminum looking good and functioning properly:
- Clean the surface of your aluminum regularly using a mild detergent solution or warm water with a soft cloth.
- If you need to remove tough stains or rust from your aluminum, mix one part vinegar with two parts water and apply it with a soft brush. Scrub gently until the stain has been removed and then rinse off the vinegar solution with plenty of clean water.
- To prevent corrosion, applying an appropriate sealant can be very helpful. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when applying any sealant to your aluminum.
- Avoid using abrasive cleaning products or tools as they can scratch the surface of your aluminum and reduce its lifespan.

By following these tips, you can keep your aluminum looking great and help it last longer!
Alternatives to Titanium and Aluminum
While titanium and aluminum are two of the most popular metals used in a variety of applications, they are not the only options. Steel is another frequently used metal with its own unique qualities. It has an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and can be heat treated to produce different levels of hardness and ductility. Stainless steel is an alloy that combines iron, chromium (which makes it resistant to rust), and other elements such as carbon or nickel. These properties make stainless steel ideal for medical devices, surgical instruments, kitchen appliances, automotive components, marine equipment, and food processing machinery.
Copper is also widely used due to its electrical conductivity. Additionally, copper has antimicrobial properties which make it suitable for use in areas with high hygiene requirements, such as hospitals and food processing facilities. Copper alloys also offer a range of attractive colors which make them popular in both industrial and decorative applications.
Other metals such as nickel, cobalt, zinc, magnesium, and even rare earth elements can be used for specific purposes depending on the desired properties. Ultimately, the metal that is best for any given application will depend on its particular requirements. The strength and weight needed for support structures will likely require titanium or aluminum while electrical applications might call for copper alloys or steel.
Applications of Titanium
Titanium has a wide range of industrial applications due to its unique physical and chemical properties. It is used in aircraft, spacecraft, medical implants, sporting equipment, jewelry, watches and many other products.
In the aerospace industry, titanium is used for fuselage structures and engines because it has excellent corrosion resistance. Titanium is also used in automotive engines due to its strength-to-weight ratio as well as its ability to withstand high temperatures.
In the medical field, titanium is often used for prosthetics and replacement joints because it can be easily formed into complex shapes without diminishing its strength or biocompatibility.
Titanium can also be alloyed with other metals such as aluminum or iron to create stronger materials with different properties that may suit specific applications.
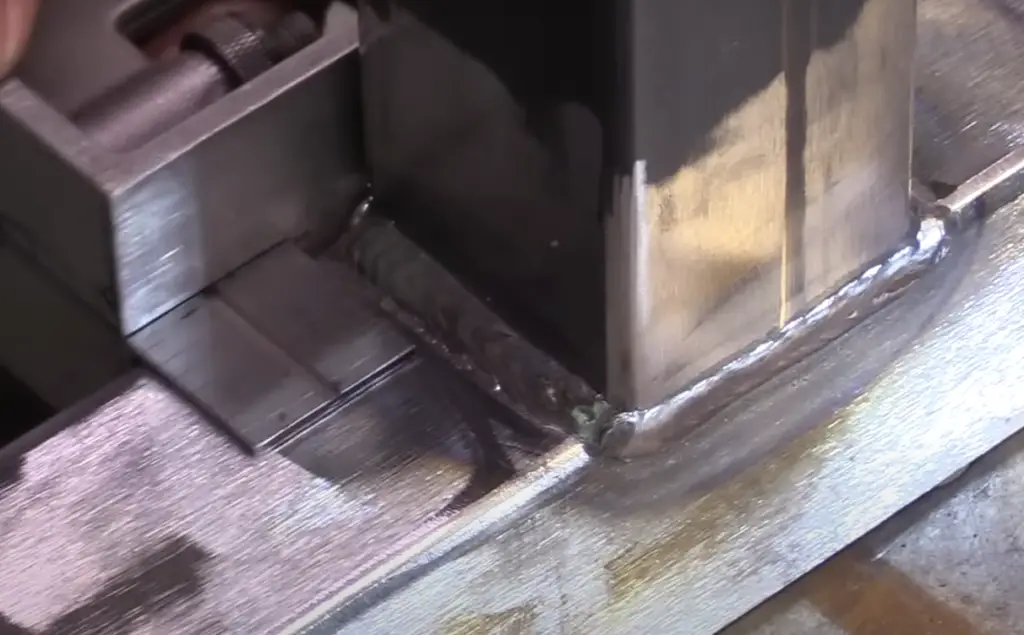

It is also used in jewelry making due to its durability and low reactivity, which helps prevent discoloration over time. Finally, titanium is often used to create watches because of its light weight and strength.
Overall, titanium has many industrial uses and continues to be one of the most versatile metals available today. While it may not always be the best material for every job, its unique properties make it a viable option for a wide variety of applications. Therefore, when considering what type of metal to use for a particular purpose, titanium should definitely be taken into consideration due to its remarkable properties and availability on the market.
Applications of Aluminum
Aluminum is a popular metal used in various industries and applications because it’s lightweight, highly resistant to corrosion, and strong. In the construction industry, aluminum is often used for window frames, siding, roofing, gutters, and other building components. It’s also employed in transportation due to its low weight and high strength-to-weight ratio.
Aluminum is commonly found in aircraft components such as wings and fuselage panels. Automotive manufacturers use aluminum to build vehicle bodies that are lighter yet stronger than traditional steel vehicles.
Other common applications of aluminum include packaging materials (tins or cans), kitchenware (pots and pans), consumer electronics (computers and phones), appliances (washing machines), medical equipment (wheelchairs) and more.
Challenges of Using Titanium
Titanium has some challenges when used in different applications. First, it is quite expensive to obtain compared to other metals such as aluminum. As a result, it may not always be the most cost-effective choice for certain projects.
Second, titanium is difficult to machine and shape due to its strength and hardness; specialized tools and processes are usually required for machining titanium components.
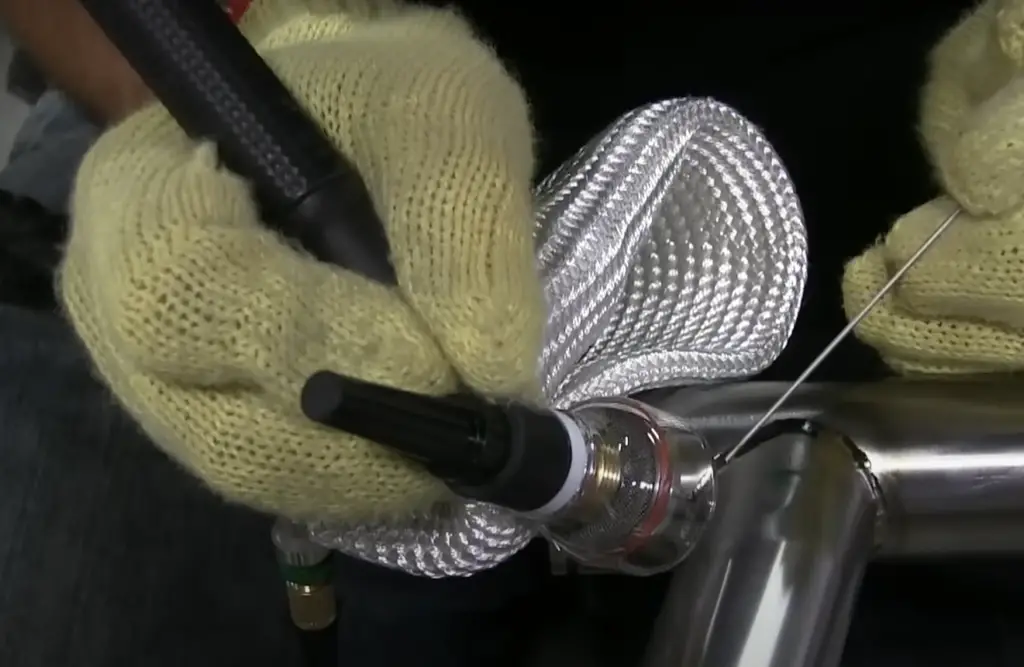
Third, welding titanium can be difficult; special techniques must be employed in order to get satisfactory results from welding titanium components together.
Finally, titanium is highly corrosion resistant which means that parts made of this metal require more maintenance than parts made of other materials like aluminum. [5]
Challenges of Using Aluminum
While aluminum is a very versatile metal, it has its drawbacks. It is not as strong or durable as titanium and can be easily bent or distorted under pressure. Aluminum also tends to corrode faster than other materials, making it more prone to rust and corrosion over time.

Additionally, aluminum needs special care when welding and machining since it melts at lower temperatures than many metals. This makes working with aluminum more difficult and time-consuming.
On the other hand, titanium is much stronger and harder than aluminum, making it less likely to bend or distort when exposed to high amounts of pressure or stress. It is also resistant to corrosion from extreme weather conditions, meaning that it will last for longer periods of time before needing maintenance or replacement. Titanium is also easier to weld and machine than aluminum, making it simpler to work with.
Overall, when comparing titanium and aluminum, titanium is usually the better option due to its superior strength and durability. Although it may cost more upfront, titanium will save money in the long run since it won’t need as much maintenance or replacement. For applications where strength and durability are paramount, titanium should be chosen over aluminum.
Tips on Using Titanium and Aluminum
When it comes to choosing a metal for your project, there are many factors to consider. While titanium and aluminum may seem like similar choices, they have some key differences that could make one or the other more suitable depending on your goals. To help you decide which is better for your needs, here are some tips on using titanium and aluminum:
- If you’re looking for lightweight strength and durability, aluminum is usually a better choice than titanium. Aluminum is considerably lighter than titanium but retains its strength over time. It’s also easier to work with if you need to cut or shape it into specific shapes or sizes.
- Titanium has superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making it a great choice in areas where the metal may be exposed to moisture or harsh chemicals. It’s also non-magnetic and has a higher melting point, so it can handle intense heat better than aluminum.
- Titanium is more expensive than aluminum, but its superior strength and other unique properties make it worth the investment in many cases.
- When used in aircraft design, titanium is generally stronger and more resistant to fatigue than aluminum at high altitudes where temperatures are low. However, this comes with an added cost for machining and fabrication that may not be necessary if you’re using it for other applications.
- If your project involves welding or soldering, aluminum is usually easier to work with as titanium requires special torches due to its high melting point.

No matter which metal you choose, understanding the differences between titanium and aluminum can help you make the best decision for your project. Whether your needs are strength, corrosion resistance or cost-effectiveness, one of these two metals will likely be a great option. [6]
FAQ
Why is aluminum better than titanium?
Aluminum is a light-weight metal with good corrosion resistant properties. It can be used for a range of applications, from aerospace to automotive. Aluminum is also easier and cheaper to fabricate than titanium, meaning it can be produced quickly and at a low cost. Compared to titanium, aluminum has far superior strength-to-weight ratio which makes it a more attractive option in some cases. Additionally, aluminum alloys can offer greater flexibility when it comes to engineering components due to the fact that they are available in various degrees of hardness or softness.
What are the advantages of titanium?
Titanium offers excellent corrosion resistance and is highly durable over time, making it an ideal choice for many industrial applications where long-term performance is a must. Titanium is also stronger than aluminum, so it can withstand higher forces and temperatures while still maintaining its structural integrity. In addition, titanium alloys are available in different strength grades to meet specific requirements and needs. Finally, titanium is resistant to wear and tear over time, making it a great choice for components that have to perform in challenging or harsh environments.
What are the main differences between aluminum and titanium?
The key difference between aluminum and titanium lies in their respective strengths: Aluminum has a greater strength-to-weight ratio than titanium but lacks the same levels of corrosion resistance and durability as its counterpart. Additionally, due to the fact that titanium is harder to fabricate than aluminum, it generally tends to be more expensive. Finally, aluminum has a wider range of alloys available for different applications compared to titanium which only offers select grades of strength.
Which is stronger, titanium or aluminum?
The answer may depend on the type of application. Both materials are durable and strong, but in certain circumstances one is better than the other.Titanium is a very strong metal, with a tensile strength of about 460 MPa (megapascals). It is also lightweight, which makes it desirable for aircraft and automotive applications. Titanium has excellent corrosion resistance properties due to its protective oxide layer that forms when exposed to air or water. This makes it an ideal choice for parts that will be exposed to high humidity or saltwater environments.
Aluminum also has good corrosion resistance properties and is very easy to work with. While it may not be as strong as titanium, aluminum can be heat-treated and strengthened for specific applications.Which is better: aluminum or stainless steel?
The answer will depend on the application. Aluminum is light and heat-treatable, making it suitable for certain applications where weight savings are important. However, stainless steel offers superior strength and corrosion resistance properties, making it more suitable for demanding environments. Both materials have their advantages and disadvantages depending on the application. Careful consideration of your requirements will help you decide which material is best suited to your needs.
Is titanium the best metal?
The short answer is, it depends on what you are looking for. Titanium has many advantages over aluminum, but it comes with a much higher price tag and can be more difficult to work with. Titanium is incredibly strong and lightweight compared to aluminum, making it an ideal choice for applications that require the metal to be durable and lightweight. It also has excellent corrosion resistance, meaning that it won’t rust or corrode in most environments. Additionally, titanium has great thermal properties which make it suitable for use in high temperature environments. On the other hand, aluminum is less expensive and easier to work with than titanium. It’s not as strong as titanium, so it may not always be able to handle the same loads, but it is still a very durable metal. Aluminum also has good corrosion resistance and thermal properties, although not quite as good as titanium.
Useful Video: So Which is Heavier? Titanium or Aluminium
Conclusion
When it comes to weight, durability, and corrosion resistance, titanium is generally the superior metal. However, aluminum does have its advantages when it comes to cost and availability. Ultimately, which metal is best depends on the application. If you need a lightweight material that won’t corrode easily and don’t mind paying more for it, titanium is probably your best bet. On the other hand, if cost or availability are priorities for your project, aluminum may be a better choice. No matter which metal you choose for your project, make sure you do your research so you pick the material that meets all of your needs.
References:
- https://www.rapiddirect.com/blog/titanium-vs-aluminum/
- https://waykenrm.com/blogs/titanium-vs-aluminum/
- https://www.protolabs.com/resources/blog/titanium-vs-aluminum-workhorse-metals-for-machining-and-3d-printing/
- https://blog.thepipingmart.com/metals/titanium-vs-aluminum-a-comparison/
- https://www.dekmake.com/titanium-vs-aluminum/
- https://blog.ansi.org/2020/03/titanium-vs-steel-aluminum/