So you want to weld copper? That’s great! Copper is a fantastic material to work with, and it can be welded using a variety of methods. This blog post will discuss the different methods that can be used to weld copper, as well as the benefits and drawbacks of each method. It will also provide some tips for welding copper effectively.
Properties of Copper and its Alloys to be Aware of When Welding
High thermal conductivity
One of the most important properties of copper and its alloys to be aware of when welding is its high thermal conductivity. Since these metals have such a high rate of heat transfer, welding them can prove to be extremely difficult.

To effectively weld copper and its alloys, one needs to ensure that they are properly preheated before welding and that they maintain an even temperature throughout the entire welding process.
High electrical conductivity
Another property of copper and its alloys is their high electrical conductivity. This makes it ideal for use in electronics as well as other applications where electricity flow must be maintained within certain parameters. When welding copper and its alloys, this property should be taken into consideration to guarantee that electrical components are not damaged by the welding process.
High ductility
Copper and its alloys also have a high degree of ductility. This means that they can be bent, shaped, and manipulated without breaking or cracking. This makes them ideal for use in construction projects where flexibility is needed. When welding copper and its alloys, it is important to keep this property in mind to ensure that the welds do not crack due to excessive bending or shaping.
High corrosion resistance
Copper and its alloys also offer excellent corrosion resistance qualities.
When welding copper and its alloys, it is important to be aware of the corrosion resistance of the metals to ensure that they are not compromised during the welding process.High melting point
Copper and its alloys have a high melting point. This means that it can withstand extremely high temperatures without breaking down or losing its strength and integrity. This makes them ideal for use in extreme conditions where other metals may fail such as in foundries or when exposed to continuous heat sources. When welding copper and its alloys, it is essential to ensure they reach their appropriate melting temperature before continuing with the welding process.
A high thermal expansion coefficient
Copper and its alloys have a high thermal expansion coefficient. This means that when exposed to heat, the metals will expand more quickly than other metals. When welding copper and its alloys, it is essential to consider this property as the increased rate of expansion can lead to cracks in the welds if not properly taken care of.
Strength
Copper and its alloys are strong metals. They have excellent strength characteristics that make them ideal for use in applications where strength is essential such as in automotive components or aerospace engineering.

When welding copper and its alloys, it is important to ensure that the welds maintain their integrity during the process and that they are properly cooled afterward to guarantee maximum strength [1].
Different Methods for Welding Copper
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Gas metal arc welding (GMAW), commonly referred to as MIG welding, is a process that has seen widespread use in the welding of copper alloys. The process uses an electric arc formed between the workpiece and a consumable electrode, which is made from wire that is continuously fed from a spool and directed at the weld joint by a MIG gun. A shielding gas is also used to protect the weld pool from contamination.
GMAW offers several advantages when it comes to welding copper alloys. It’s relatively fast compared to other processes, and since it doesn’t require any additional filler material, it’s easy to control heat input during welding, resulting in less distortion of the workpiece.
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Submerged arc welding (SAW) is a process that has been used for many years to weld copper alloys. The process uses an electric arc formed between the workpiece and a consumable electrode, which is made from wire and passed through a submerged flux-filled bath. The flux forms a slag layer on top of the weld pool, protecting it from contamination as well as helping to promote fusion between the two materials.
It’s also possible to achieve highly dependable welds with minimal distortion.Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), commonly referred to as TIG welding, is a process that has seen widespread use in the welding of copper alloys. The process uses an electric arc formed between the workpiece and a non-consumable tungsten electrode, which is directed at the weld joint by a TIG torch. A shielding gas is also used to protect the weld pool from contamination.

GTAW offers several advantages when it comes to welding copper alloys. Its high precision makes it ideal for applications where accuracy and repeatability are critical, while its low heat input reduces distortion of the workpiece. This process can be used with or without additional filler material depending on the application, providing greater flexibility when it comes to weld joint design.
Manual Metal Arc Welding (MMAW)
Manual metal arc welding (MMAW), also known as stick welding, is a process that has been used for many years to weld copper alloys. The process uses an electric arc formed between the workpiece and a consumable electrode, which is made from flux-coated rods that are melted by the heat of the arc. This results in a slag layer on top of the weld pool, protecting it from contamination as well as helping to promote fusion between the two materials.
MMAW offers several advantages when it comes to welding copper alloys, including portability, ease of use, and low cost. It can be used in any position and with or without additional filler material depending on the application, providing greater flexibility when it comes to weld joint design [2].
The Key Steps in Welding Copper
Prepare the Metal: Before starting any welding project, it’s important to clean the copper and remove any dirt and debris that may be present on the surface of the metal. This can be done through sanding or buffing with a wire brush.
Preheat the Metal: Copper can become brittle when heated quickly, so it’s important to preheat the metal before welding begins.
This will help to ensure a strong weld and reduce warping due to heat stress.
Select an Appropriate Welding Rod: Different kinds of welding rods are used for different purposes; so make sure you select one that is appropriate for working with copper specifically.
Set Up the Welder: Once all of your preparations are complete, you can begin to set up the welder. Start by setting the current, voltage and wire speed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Strike an Arc: When everything is ready, it’s time to strike an arc. Hold the welding rod at a 45-degree angle from the surface of the metal and make sure that it doesn’t come into contact with anything else while you work.
Monitor Your Progress: As you weld, keep an eye on your progress and adjust as necessary if things don’t seem right. You may need to increase or decrease your heat settings depending on how well your weld is progressing.
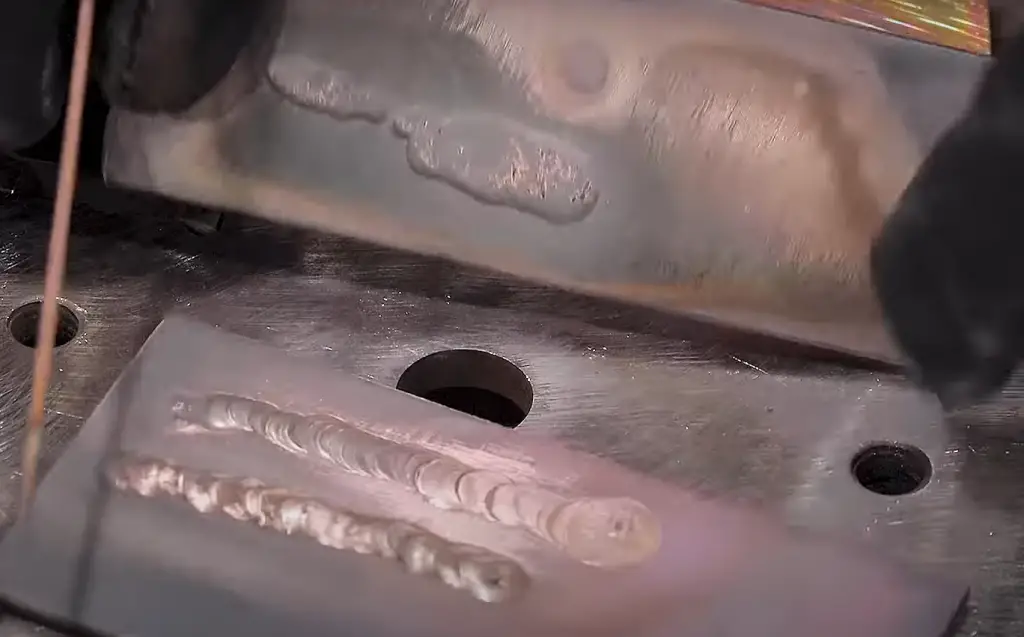

Clean and Inspect: To wrap up the process, it’s important to thoroughly clean the area where you were working and inspect your weld for any defects or inconsistencies. If everything looks good, you’re ready to move on to the next project [3]!
Safety Tips when Working with Copper Alloys
When working with copper and its alloys, safety should always be a priority. The following are some safety tips to keep in mind when working with copper and its alloys:
- Wear proper protective gear – When working with copper and its alloys, it is important to wear the appropriate protective gear to protect yourself from any potential hazards. This includes long-sleeved shirts and pants, safety glasses, gloves, and a respirator if necessary.
- Make sure your work area is clean – Copper dust can cause respiratory problems so it is important to keep your work area as clean as possible by using wet rags or vacuuming up dust particles. Use masking tape on surfaces you don’t want to be contaminated with copper dust.
- Ensure proper ventilation – When working with copper and its alloys, it is important to make sure there is proper ventilation to reduce your exposure to any potential fumes that may be released while working with the material.
- Wear protective clothing when welding – It is important to wear flame-resistant clothing such as leather gloves and long-sleeved shirts when welding copper or its alloys.
- Store copper safely – Copper should always be stored in a cool, dry place away from any sources of heat or sparks that could ignite a fire. Additionally, ensure that the storage containers for copper are properly labeled and sealed so they don’t become a source of contamination for other materials.
By following these safety tips, you can help ensure a safe and productive work environment when working with copper and its alloys. Safety is always the top priority when working with any type of material, so be sure to follow these guidelines to keep yourself and those around you safe!
Failing to do so can result in serious injury or even death. Always make sure that the area is properly monitored at all times when working with copper and its alloys.FAQ
Is it hard to weld copper?
Welding copper can be difficult due to its higher melting point compared to other metals. It requires a high amount of skill and patience to make clean, strong welds. Good preparation is also essential when working with copper, as the surface must be cleaned and properly prepared before welding takes place. With these tips in mind, the right tools, and plenty of practice, welding copper can become a highly achievable task for experienced welders.
When can’t you weld copper?
Due to its high melting point, it’s not recommended to weld copper directly onto stainless steel or other ferrous metals. This is because the metal could become contaminated with iron during the welding process and cause a variety of problems. Copper can be joined onto stainless steel by using a brass filler material or an appropriate heat-resistant alloy.
What type of welding is best for copper?
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding is generally considered to be the best technique when working with copper. It produces strong, clean welds and allows for precise control over the heat input and speed of the weld.
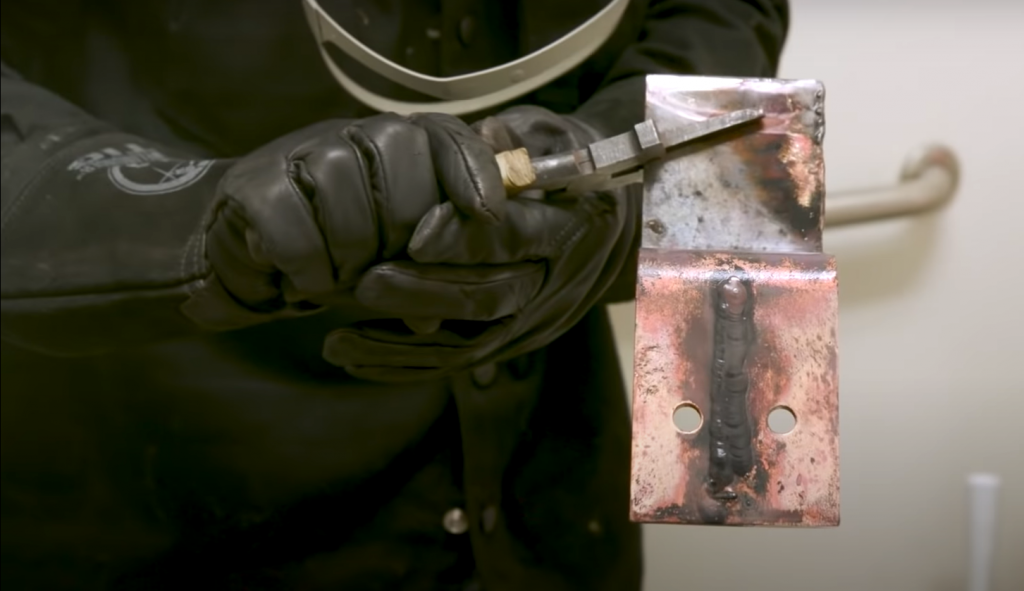

TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding is another option that offers very fine control over the arc but requires more practice and skill to master. Both techniques work well for welding copper but MIG is often the preferred choice due to its simplicity and ease of use.
What safety measures should be taken when welding copper?
When working with copper, it’s important to take all proper safety precautions. Wear appropriate protective clothing such as a welding helmet, gloves, long-sleeved shirts, and pants. Additionally, make sure you are working in a well-ventilated area to reduce exposure to toxic fumes emitted during the process. Finally, always double-check your welds before use and follow any instructions provided by your equipment manufacturer or supplier.
Does weld stick to copper?
Various types of welding sticks, or electrodes, can be used to weld copper. These include mild steel, stainless steel, and nickel electrodes. Each type has unique properties that make it better suited for certain types of welding tasks. For example, mild steel electrodes are great for general-purpose welding while stainless steel is ideal for joining dissimilar metals together. Nickel electrodes provide the highest level of corrosion protection when working with copper and other non-ferrous metals. For more information on welding sticks and their applications, consult with a qualified professional before beginning any project.
How do you weld copper with copper?
When welding copper to copper, it’s best to use a MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welder. This type of welding machine produces strong, clean welds and allows for precise control over the heat input and speed. It also works well for creating joints with small beads, which is essential when working with thin copper materials. To ensure the highest quality result, make sure that both copper pieces are properly cleaned before welding, and always double-check your welds for accuracy before use.
How do you prepare copper for welding?
Before beginning any welding project involving copper, it’s important to properly prepare the material beforehand. This includes cleaning off all dirt, dust, oil, or other contaminants from the surface of the copper. It’s also important to make sure that the edges of the pieces are properly beveled and rounded off to ensure a consistent, even weld. Finally, when using MIG welding, it’s necessary to use shielding gas to protect the material from oxidation. Following these steps will help ensure a successful welding project with copper.
Can you connect copper without soldering?
Yes, copper can be connected without soldering. The most common methods for doing so are welding (MIG or TIG) and crimping. Welding offers the strongest joint but requires more practice and skill to master, while crimping is usually a faster, easier option that also produces fairly strong connections. Additionally, there are mechanical connectors available which require no heat or solder and provide reliable connections between copper pieces.
Useful Video: CAN YOU WELD COPPER? – not solder, not braze, but weld? spoiler….yes you can and i will show you
Conclusion
Welding copper requires a wide range of tools and materials to ensure the safety of welders and the quality of their welds. Welders need to use the appropriate type of welding machine, filler material, flux, and shielding gas for each welding job. Furthermore, welders must take extra precautions when welding copper due to its high conductivity, as improper technique can cause arcs which could be hazardous. With proper knowledge and practice, however, experienced welders should have no difficulty producing strong and reliable copper welds that meet industry standards.
References:
- https://www.forsteramerica.com/tips-welding-copper/
- https://www.brazing.com/Support/Procedures_and_techniques/CopperWeldingProcedures
- https://weldingheadquarters.com/how-to-weld-copper/